반응형
RSA 암호화 기법은 정수론 공부하면서 접하는 내용 중에 가장 흥미로운 내용이지 않을까 싶다.
오일러 정리가 무엇인지 정도만 안다면 수식을 이해하는 것도 크게 어렵지 않다.
컴퓨터로 뚝딱뚝딱 만들다보면 실생활에서 널리 쓰이는 암호를 꽤 쉽게 만들 수 있게 된다.
이번 시간에는 RSA 암호를 만들고 해독하는 기초적인 방법을 알아볼 것이다.
연애 편지를 이걸 활용해서 쓰면...... 유부남이 되긴 어렵겠지?
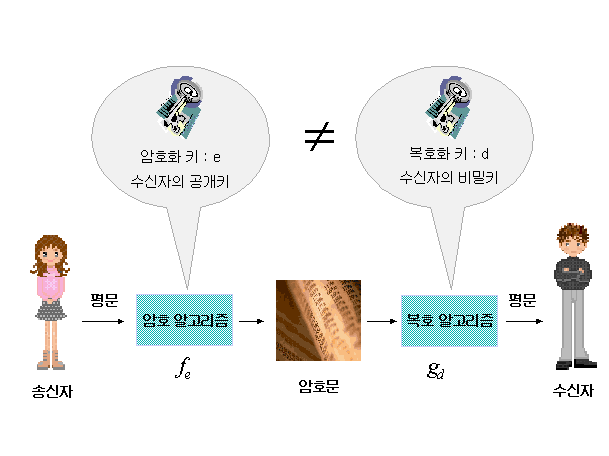
RSA는 소수의 수학적 속성을 기반으로 널리 사용되는 공개 키 암호화 시스템입니다. 다음은 Python을 사용한 RSA 암호화 및 암호 해독 프로세스에 대한 단계별 설명입니다. 키를 생성하기 위해 두 개의 256비트 소수를 사용합니다. 다음은 절차 개요입니다.
Python에서 RSA를 구현하는 단계:
1. 두 개의 큰 소수(p 및 q)를 생성합니다:
- 이는 RSA 키 생성의 기초가 됩니다. 128비트 소수를 생성하기 위해 Python의 sympy 라이브러리를 사용할 수 있습니다.
from sympy import randprime, mod_inverse
import math
# Step 1: Generate two 128-bit prime numbers
bit_length = 128
p = randprime(2**(bit_length - 1), 2**bit_length)
q = randprime(2**(bit_length - 1), 2**bit_length)2. n = p * q를 계산합니다.:
- 곱 'n'은 공개 키와 개인 키 모두에 대한 법(modulus)입니다.
# Step 2: Compute n = p * q
n = p * q3. 오일러의 전체 함수 ψ(n) = (p-1) * (q-1) 을 계산합니다.
- 이 값은 키가 수학적으로 호환되는지 확인하는 데 사용됩니다.
# Step 3: Compute Euler's totient function ϕ(n)
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)4. 공개 지수 e를 선택하세요:
- 'e' 값은 'ф(n)'과 서로소여야 하며 일반적으로 효율성을 위해 65537과 같은 작은 값으로 설정됩니다.
# Step 4: Choose a public exponent e
e = 65537 # Commonly used public exponent
# Ensure e is coprime with ϕ(n)
if math.gcd(e, phi) != 1:
raise ValueError("e and ϕ(n) are not coprime. Choose a different e.")5. 비공개 지수 d를 계산합니다:
- 값 d는 e mod ф(n)의 모듈러 곱셈의 역수입니다.
# Step 5: Compute the private exponent d
d = mod_inverse(e, phi)
# Display the generated keys
print(f"""Public Key:
(
e={e},
n={n}
)""")
print(f"""Private Key:
(
d={d},
n={n}
)""")Public Key:
(
e=65537,
n=53235866521041869581214641922864588635087121640405913511888426141510024216947
)
Private Key:
(
d=22222158481714793569026488229302631357514840210514834090911250279688138012329,
n=53235866521041869581214641922864588635087121640405913511888426141510024216947
)6. 메시지 암호화:
- 'cipher = (message ^ e) % n' 공식을 사용하세요.
# Step 6: Encryption
def encrypt(message, e, n):
# Convert the message to an integer
message_int = int.from_bytes(message.encode('utf-8'), byteorder='big')
# Encrypt using the formula: cipher = (message^e) % n
cipher = pow(message_int, e, n)
return cipher7. 메시지 암호 해독:
- 'decrypted_message = (cipher ^ d) % n' 공식을 사용하세요.
# Step 7: Decryption
def decrypt(cipher, d, n):
# Decrypt using the formula: message = (cipher^d) % n
message_int = pow(cipher, d, n)
# Convert the integer back to a string
message = message_int.to_bytes((message_int.bit_length() + 7) // 8, byteorder='big').decode('utf-8')
return message
적용 예시
# Example usage
message = "Hello, RSA!"
print(f"Original Message: {message}")
# Encrypt the message
cipher = encrypt(message, e, n)
print(f"Encrypted Message: {cipher}")
# Decrypt the message
decrypted_message = decrypt(cipher, d, n)
print(f"Decrypted Message: {decrypted_message}")Original Message: Hello, RSA!
Encrypted Message: 17163130120416272182862379462485169348139978913280676801027913333475892282845
Decrypted Message: Hello, RSA!요점 설명:
- 소수 생성:
- sympy.randprime 함수를 사용하여 큰 소수를 생성합니다. 이는 암호화 보안을 보장합니다.
- 공개 및 개인 키:
- 공개키는 '(e, n)'이며 공개적으로 공유됩니다.
- 개인키는 (d, n)이므로 비밀로 유지해야 합니다.
- 메시지 변환:
- 메시지는 암호화 전에 정수로 변환되고 암호 해독 후에는 다시 문자열로 변환됩니다.
- 지수화:
- 모듈식 지수화는 암호화 및 암호 해독에 사용됩니다. Python의 pow(base, exp, mod)는 이에 최적화되어 있습니다.
참고:
- 메시지 길이:
- 메시지 크기는 법 'n' 보다 작아야 합니다. 대용량 메시지의 경우 RSA는 일반적으로 대칭 암호화와 결합됩니다.
- 보안:
- 실제 애플리케이션의 경우 RSA를 처음부터 구현하는 대신 'pycryptodome'과 같이 잘 테스트된 라이브러리를 사용하세요.
반응형
'Computer > 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| RSA 암호화 기법 (2): 왜 해독하기 어려운가? (5) | 2025.01.23 |
|---|
